General
Get the current user
Note this will not get the user entity, but rather a user proxy with basic info but no fields or entity-specific data.
$user = \Drupal::currentUser();$user = \Drupal\user\Entity\User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());Or
use \Drupal\user\Entity\User;
$user = User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());Get the logged in user name and email
$username = \Drupal::currentUser()->getAccountName();or
$account_proxy = \Drupal::currentUser();
//$account = $account_proxy->getAccount();
// load user entity
$user = User::load($account_proxy->id());
$user = User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());
$name = $user->get('name')->value;$email = \Drupal::currentUser()->getEmail();or
$user = User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());
$email = $user->get('mail')->value;Get the current Path
\Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath() returns the current relative path. For node pages, the return value will be in the form "/node/32" For taxonomy "taxonomy/term/5", for user "user/2" if it exists otherwise it will return the current request URI.
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();
// Get the alias (i.e. if the user entered node/123, this will return e.g. /bicycles/super-cool-one)
$alias = \Drupal::service('path_alias.manager')->getAliasByPath($current_path);
// Get path with query string e.g. /abc/def/123?a=fred.
$current_path_and_alias = \Drupal::request()->getRequestUri();
// Get path e.g. /abc/def/123
$current_path = Url::fromRoute('<current>')->toString();Lots more on the Drupal Stackexchange
Check if you are on the Front page
$is_front = \Drupal::service('path.matcher')->isFrontPage();The above statement will return either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE means you are on the front page.
Check if the site is in system maintenance mode
$is_maint_mode = \Drupal::state()->get('system.maintenance_mode');Retrieve query, get or post parameters
For get variables use:
$query = \Drupal::request()->query->get('name');For post variables use:
$name = \Drupal::request()->request->get('name');For all items in a get:
$query = \Drupal::request()->query->all();
$search_term = $query['query'];
$collection = $query['collection'];Note
Drupal will cache requests so render arrays need cache contexts specified correctly in order to successfully retrieve those parameters. See Caching
Convert TranslatableMarkup to a string
To convert a TranslatableMarkup object to a string, use either the render() or __toString() method. This example shows the values array with an element 'save' which is a TranslatableMarkup object. These will return Save Citation.

$values['save']->render();
// Or.
$values['save']->__toString();Get Node URL alias or Taxonomy Alias by Node id or Term ID
Sometimes we need a relative path and sometimes we need an absolute path. There is an $options parameter in the fromRoute() function where specify which you need.
Parameters:
- absolute true will return absolute path.
- absolute false will return relative path.
Returns the node alias. Note. If a nice url is not set using pathauto, you get /node/1234
use Drupal\Core\Url;
$options = ['absolute' => true]; //false will return relative path.
$url = Url::fromRoute('entity.node.canonical', ['node' => 1234], $options);
$url = $url->toString(); // make a string
// OR
$node_path = "/node/1";
$alias = \Drupal::service('path_alias.manager')->getAliasByPath($node_path);
// OR
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();To get the full path with the host etc. this returns: https://ddev93.ddev.site/node/1
$host = \Drupal::request()->getSchemeAndHttpHost();
$url = \Drupal\Core\Url::fromRoute('entity.node.canonical',['node'=>$lab_home_nid]);
$url_alias = $url->toString();
$full_url = $host . $url->toString();You can get the hostname, e.g. "drupal8.local", directly from the getHost() request with:
$host = \Drupal::request()->getHost();Taxonomy alias
Return taxonomy alias
$options = ['absolute' => true]; //false will return relative path.
$url = Url::fromRoute('entity.taxonomy_term.canonical', ['taxonomy_term' => 1234], $options);Get current Path
For node pages this will return node/{node id}, for taxonomy taxonomy/term/{term id}, for user user/{user id} if exists otherwise it will return the current request URI.
$currentPath = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();Get current nid, node type and title
There are two ways to retrieve the current node -- via the request or the route
$node = \Drupal::request()->attributes->get('node');
$nid = $node->id();OR
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
$nodeType = $node->bundle();
$nodeTitle = $node->getTitle();
}If you need to use the node object in hook_preprocess_page on the preview page, you will need to use the node_preview parameter, instead of the node parameter:
function mymodule_preprocess_page(&$vars) {
$route_name = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getRouteName();
if ($route_name == 'entity.node.canonical') {
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
}
elseif ($route_name == 'entity.node.preview') {
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node_preview');
}And from https://drupal.stackexchange.com/questions/145823/how-do-i-get-the-current-node-id when you are using or creating a custom block then you have to follow this code to get current node id. Not sure if it is correct.
use Drupal\Core\Cache\Cache;
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
$nid = $node->id();
}
// for cache
public function getCacheTags() {
//With this when your node changes your block will rebuild
if ($node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node')) {
//if there is node add its cachetag
return Cache::mergeTags(parent::getCacheTags(), ['node:' . $node->id()]);
}
else {
//Return default tags instead.
return parent::getCacheTags();
}
}
public function getCacheContexts() {
//if you depend on \Drupal::routeMatch()
//you must set context of this block with 'route' context tag.
//Every new route this block will rebuild
return Cache::mergeContexts(parent::getCacheContexts(), ['route']);
}How to check whether a module is installed or not
$moduleHandler = \Drupal::service('module_handler');
$module_name = “views”;
if ($moduleHandler->moduleExists($module_name)) {
echo "$module_name installed";
}
else {
echo "$module_name not installed";
}Get current Route name
Routes are in the form: view.files_browser.page_1, test.example or test.settings_form
E.g from test.routing.yml
test.example:
path: '/test/example'
defaults:
_title: 'Example'
_controller: '\Drupal\test\Controller\TestController::build'
requirements:
_permission: 'access content'
test.settings_form:
path: '/admin/config/system/test'
defaults:
_title: 'Test settings'
_form: 'Drupal\test\Form\SettingsForm'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer test configuration'This will return Drupal route. It returns entity.node.canonical for the nodes, system.404 for the 404 pages, entity.taxonomy_term.canonical for the taxonomy pages, entity.user.canonical for the users and custom route name that we define in modulename.routing.yml file.
$current_route = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getRouteName();Get the current page title
You can use this in a controller, to return the current page title.
$request = \Drupal::request();
if ($route = $request->attributes->get(\Symfony\Cmf\Component\Routing\RouteObjectInterface::ROUTE_OBJECT)) {
$title = \Drupal::service('title_resolver')->getTitle($request, $route);}Get the current user
Note this will not get the user entity, but rather a user proxy with basic info but no fields or entity-specific data.
$user = \Drupal::currentUser();To get the user entity, use this which gets the user service (\Drupal::currentUser()), gets the uid (->id()), then calls load() to load the real user object.
$user = \Drupal\user\Entity\User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());Or
use \Drupal\user\Entity\User;
$user = User::load(\Drupal::currentUser()->id());Check if you are on the Front page
This will return true for the front page otherwise false.
$is_front = \Drupal::service('path.matcher')->isFrontPage();Retrieve URL argument parameters
You can extract the url arguments with
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();
$path_args = explode('/', $current_path);
$term_name = $path_args[3];For https://txg.ddev.site/newsroom/search/?country=1206

Get Current Language in a constructor
In dev1 - /modules/custom/iai_wea/src/Plugin/rest/resource/WEAResource.php we create the WeaResource class and using dependency injection, get the LanguageManagerInterface service passed in, then we call getgetCurrentLanguage(). This allows us to later retrieve the node
class WEAResource extends ResourceBase {
/**
* @var \Drupal\Core\Language\Language
*/
protected $currentLanguage;
/**
* WEAResource constructor.
*
* @param array $configuration
* @param string $plugin_id
* @param mixed $plugin_definition
* @param array $serializer_formats
* @param \Psr\Log\LoggerInterface $logger
* @param \Drupal\Core\Language\LanguageManagerInterface $language_manager
*/
public function __construct(array $configuration, string $plugin_id, mixed $plugin_definition, array $serializer_formats, \Psr\Log\LoggerInterface $logger, LanguageManagerInterface $language_manager) {
parent::__construct($configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition, $serializer_formats, $logger);
$this->currentLanguage = $language_manager->getCurrentLanguage();
}
}Later in the class, we can retrieve the correct language version of the node:
public function get($id) {
if ($node = Node::load($id)) {
$translatedNode = $node->getTranslation($this->currentLanguage->getId());Of course, you can also get the language statically by using:
Global $language = Drupal::languageManager()->getLanguage(Language:TYPE_INTERFACE)This is part of the packt publishing Mastering Drupal 8 module development video series: https://www.packtpub.com/product/mastering-drupal-8-development-video/9781787124493
NOTE
To test this in modules/custom/pseudo_client/get/
php -S localhost:8888and put this in a browser:
http://localhost:8888/get_item_from_drupal_core.php?domain=dev1&item=2716or
http://localhost:8888/get_items_from_custom_code.php?domain=dev1OR just put this in browser without running php -S:
http://dev1/iai_wea/actions/2716?_format=jsonAdd a variable to any page on the site
In the .theme file of the theme, add a hook_preprocess_page function like in themes/custom/dprime/dprime.theme:
function dprime_preprocess_page(&$variables) {
$language_interface = \Drupal::languageManager()->getCurrentLanguage();
$variables['footer_address1'] = [
'#type'=>'markup',
'#markup'=>'123 Disk Drive, Sector 439',
];
$variables['footer_address2'] = [
'#type'=>'markup',
'#markup'=>'Austin, Texas 78759',
];Then in the template file e.g. themes/custom/dprime/templates/partials/footer.html.twig
<div class="cell xlarge-3 medium-4">
<address>
{{ footer_address1 }}<br />
{{ footer_address2 }}<br />
Campus mail code: D9000<br />
<a href="mailto:abc@example.com">abc@example.com </a>
</address>
</div>Add a variable to be rendered in a node.
From dev1 custom theme burger_burgler.
Here two vars stock_field and my_custom_field are added and will be rendered by a normal node twig file. The function hook_preprocess_node is in the .theme file at themes/custom/burger_burgler/burger_burgler.theme.
function burger_burgler_preprocess_node(&$variables) {
$variables['content']['stock_field'] = [
'#type'=>'markup',
'#markup'=>'stock field here',
];
$variables['content']['my_custom_field'] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => 'Hello - custom field here',
];
}If you've tweaked your node twig template, you'll need to reference like this:
<div class="stock-field-class">
{{ content['stock_field'] }}
</div>Note. You can always just add a variable like
$variables['abc'] = 'hello';which can be referenced in the template as
{{ abc }}or
{{ kint(abc) }}Add a bunch of variables to be rendered in a node
You can easily grab the node from the $variables with:
$node = $variables['node'];Then to access a field in the node, you can just specify them by:
$node->field_ref_aof
$node->field_ref_topicHere we grab a bunch of variables, cycles through them (for multi-value fields, which most of them are and build an array that can be easily rendered by twig:
From: themes/custom/txg/txg.theme
function txg_preprocess_node(&$variables) {
$view_mode = $variables['view_mode']; // Retrieve view mode
$allowed_view_modes = ['full']; // Array of allowed view modes (for performance so as to not execute on unneeded nodes)
$node = $variables['node'];
if (($node->getType() == 'news_story') && ($view_mode == 'full')) {
$aofs = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_aof, 'aof', 'target_id');
$units = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_unit, 'unit', 'target_id');
$audiences = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_audience, 'audience', 'target_id');
$collections = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_program_collection, 'collection', 'target_id');
$topics = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_topic, 'topic', 'target_id', 'taxonomy');
$continents = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_continent, 'continent', 'value', 'list');
$countries = _txg_multival_ref_data($node->field_ref_country, 'country', 'target_id');
$related_news_items = array_merge($topics, $aofs, $units, $audiences, $collections, $continents, $countries);
$variables['related_news_items'] = $related_news_items;
}
}
/**
* Returns array of data for multivalue node reference fields
* ref_field = entity reference field
* param_name = parameter name to be passed as get value
* value_type = indicates which field to retrieve from database
* field_ref_type = variable to determine type of reference field
* field_term_category =
*/
function _txg_multival_ref_data($ref_field, $param_name, $value_type, $field_ref_type = 'node') {
$values = [];
foreach($ref_field as $ref) {
if ($field_ref_type == 'taxonomy') {
$term = Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('taxonomy_term')->load($ref->$value_type);
$title = $term->getName();
}
else {
$title = $value_type == 'value' ? $ref->$value_type : $ref->entity->title->value;
}
$id = $ref->$value_type;
$values[] = [
'title' => $title,
'id' => str_replace(' ', '+', $id),
'param_name' => $param_name,
];
}
return $values;
}Grabbing entity reference fields in hook_preprocess_node for injection into the twig template
You can easily pull in referenced fields by referring to them as
$node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_how_to_order->value;Where field_sf_contract_ref is the reference field, which points to an entity which has a field called field_how_to_order. Then we can jam it into the $variables array and refer to it in the twig template as {{ how_to_order }}
From web/themes/custom/dirt_bootstrap/dirt_bootstrap.theme
In function dirt_bootstrap_preprocess_node(&$variables)
if ($type === 'contract') {
if ($view_mode === 'full') {
$how_to_order_lookup = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_how_to_order_lookup->value;
$variables['how_to_order_lookup'] = $how_to_order_lookup;
$contract_type = $node->get('field_contract_type')->value;
if ($how_to_order_lookup === "Custom Text") {
if ($contract_type === "DIRT") {
$variables['how_to_order'] = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_how_to_order->value;
}
else {
$variables['how_to_order'] = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_how_to_order_custom->value;
}
}
}
}Render a list created in the template_preprocess_node()
Here we create a list in the preprocess_node custom theme burger_burgler):
function burger_burgler_preprocess_node(&$variables) {
$burger_list = [
['name' => 'Cheesburger'],
['name' => 'Mushroom Swissburger'],
['name' => 'Jalapeno bugburger'],
];
$variables['burgers'] = $burger_list;
}and render it in the twig template node--article--full.html.twig
<ol>
{% for burger in burgers %}
<li> {{ burger['name'] }} </li>
{% endfor %}
</ol>Indexing paragraphs so you can theme the first one
Posted on https://www.drupal.org/project/paragraphs/issues/2881460#comment-13291215
From themes/custom/dprime/dprime.theme
Add this to the theme:
/**
* Implements hook_preprocess_field.
*
* Provides an index for these fields referenced as {{ paragraph.index }}
* in twig template.
*
* @param $variables
*/
function dprime_preprocess_field(&$variables) {
if($variables['field_name'] == 'field_video_accordions'){
foreach($variables['items'] as $idx => $item) {
$variables['items'][$idx]['content']['#paragraph']->index = $idx;
}
}
}field_video_accordions is the name of the field that holds the paragraph you want to count.
In the twig template for that paragraph, you can use the value paragraph.index as in:
{% if paragraph.index == 0 %}
<li class="accordion-item is-active" data-accordion-item="">
{% else %}
<li class="accordion-item" data-accordion-item="">
{% endif %}Add meta tags using template_preprocess_html
Also covered at https://drupal.stackexchange.com/questions/217880/how-do-i-add-a-meta-tag-in-inside-the-head-tag
If you need to make changes to the <head> element, the hook_preprocess_html is the place to do it in the .theme file. Here we check to see that the content type is contract and then we create a fake array of meta tags and jam them into the $variables['page']['#attached']['html_head'] element. They are then rendered on the page.
/**
* Implements hook_preprocess_html().
*/
function dir_bootstrap_preprocess_html(&$variables) {
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
if ($node->getType() == 'contract') {
$brand_meta_tag[] = [[
'#tag' => 'meta',
'#attributes' => [
'name' => 'brand',
'content' => 'Dell',
]],
'Dell',
];
..
$variables['page']['#attached']['html_head'][] = $brand_meta_tag;Note that the extra "Dell" low down in the array appears to be a description of some kind -- it isn't rendered. If you don't include the second "Dell" you could rather use
$page['#attached']['html_head'][] = [$description, 'description'];For multiple tags, I had to do this version:
$brand_meta_tags[] = [[
'#tag' => 'meta',
'#attributes' => [
'name' => 'brand',
'content' => 'Dell',
]],
'Dell',
];
$brand_meta_tags[] = [[
'#tag' => 'meta',
'#attributes' => [
'name' => 'brand',
'content' => 'Apple',
]],
'Apple',
];
foreach ($brand_meta_tags as $brand_meta_tag) {
$variables['page']['#attached']['html_head'][] = $brand_meta_tag;
}And here I do a query and build some new meta tags from themes/custom/dirt_bootstrap/dirt_bootstrap.theme.
$brand_meta_tags = [];
$contract_id = $node->field_contract_id->value;
if ($contract_id) {
//Lookup dirt store brand records with this contract id.
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'sf_store_brands')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('field_contract_id', $contract_id);
$nids = $query->execute();
foreach ($nids as $nid) {
$store_brand_node = Node::load($nid);
$brand = $store_brand_node->field_brand->value;
if ($brand) {
$brand_meta_tags[] = [[
'#tag' => 'meta',
'#attributes' => [
'name' => 'brand',
'content' => $brand,
]],
$brand,
];
}
}
foreach ($brand_meta_tags as $brand_meta_tag) {
$variables['page']['#attached']['html_head'][] = $brand_meta_tag;
}
}Decoding URL encoded strings
Encoded strings have all non-alphanumeric characters except -_. replaced with a percent (%) sign followed by two hex digits and spaces encoded as plus (+) signs. This is the same way that the posted data from a WWW form is encoded, and also the same way as in application/x-www-form-urlencoded media type.
When you see strings like %20 or %E2 and you need plaintext, use urldecode().
echo urldecode("threatgeek/2016/05/welcome-jungle-tips-staying-secure-when-you%E2%80%99re-road") . "\n";
echo urldecode('We%27re%20proud%20to%20introduce%20the%20Amazing') . "\n";
//$str = "threatgeek/2016/05/welcome-jungle-tips-staying-secure-when-you%E2%80%99re-road";
//echo htmlspecialchars_decode($str) . "\n";returns:
threatgeek/2016/05/welcome-jungle-tips-staying-secure-when-you’re-road
We're proud to introduce the AmazingEncoding looks like this:
echo urlencode("threatgeek/2016/05/welcome-jungle-tips-staying-secure-when-you're-road") . "\n";returns:
threatgeek%2F2016%2F05%2Fwelcome-jungle-tips-staying-secure-when-you%E2%80%99re-roadRemote media entities
For this project, I had to figure out a way to make media entities that really were remote images. i.e. the API provided images but we didn't want to store them in Drupal
I started by looking at https://www.drupal.org/sandbox/nickhope/3001154 which was based on https://www.drupal.org/project/media_entity_flickr.
I tweaked the nickhope module (media_entity_remote_file) so it worked but it had some trouble with image styles and thumbnails
A good solution (thanks to Hugo) is:
https://www.drupal.org/project/remote_stream_wrapper_widget
https://www.drupal.org/project/remote_stream_wrapper
Hugo suggests using this to do migration:
$uri = 'http://example.com/somefile.mp3';
$file = File::Create(['uri' => $uri]);
$file->save();
$node->field_file->setValue(['target_id' => $file->id()]);
$node->save();There was no documentation so I added some.
Deprecated functions like drupal_set_message
Note
drupal_set_message() has been removed from the codebase, so you should use messenger() but you can also use dsm() which is provided by the devel contrib module. This is useful when working through a problem if you want to display a message on a site during debugging.
From https://github.com/mglaman/drupal-check/wiki/Deprecation-Error-Solutions
Before
drupal_set_message($message, $type, $repeat);After
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage($message, $type, $repeat);Block excessive crawling of Drupal Views or search results with .htaccess
From Block excessive crawling of Drupal Views or search results on Acquia.com - Jan 2024
PLACE THIS BLOCK directly after the "RewriteEngine on" line in your docroot/.htaccess or web/.htaccess file.
Sometimes, robot webcrawlers (like Bing, Huwaei Cloud, Yandex, Semrush, etc.) can attempt to crawl a Drupal View's search results pages, and could also be following links to each of the view's filtering options. This places extra load on your site. Additionally, the crawling (even if done by legitimate search engines) may not be increasing your site's visibility to users of search engines.
Therefore, we suggest blocking or re-routing this traffic to reduce resource consumption at the Acquia platform, avoid overages to your Acquia entitlements (for Acquia Search, Views & Visits, etc.), and to generally help your site perform better.
# EXAMPLE ROBOT BLOCKING CODE for Search pages or views.
# From: https://support-acquia.force.com/s/article/4408794498199-Block-excessive-crawling-of-Drupal-Views-or-search-results
# NOTE: May need editing depending on your use case(s).
#
# INSTRUCTIONS:
# PLACE THIS BLOCK directly after the "RewriteEngine on" line
# in your docroot/.htaccess file.
#
# This will block some known robots/crawlers on URLs when query arguments are present.
# DOES allow basic URLs like /news/feed, /node/1 or /rss, etc.
# BLOCKS only when search arguments are present like
# /news/feed?search=XXX or /rss?page=21.
# Note: You can add more conditions if needed.
# For example, to only block on URLs that begin with '/search', add this
# line before the RewriteRule:
# RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} ^/search
#
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} .
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} "11A465|AddThis.com|AdsBot-Google|Ahrefs|alexa site audit|Amazonbot|Amazon-Route53-Health-Check-Service|ApacheBench|AppDynamics|Applebot|ArchiveBot|AspiegelBot|Baiduspider|bingbot|BLEXBot|BluechipBacklinks|Buck|Bytespider|CCBot|check_http|cludo.com bot|contentkingapp|Cookiebot|CopperEgg|crawler4j|Csnibot|Curebot|curl|Daum|Datadog Agent|DataForSeoBot|Detectify|DotBot|DuckDuckBot|facebookexternalhit|Faraday|FeedFetcher-Google|feedonomics|Funnelback|GAChecker|Grapeshot|gobuster|gocolly|Googlebot|GoogleStackdriverMonitoring|Go-http-client|GuzzleHttp|HeadlessChrome|heritrix|hokifyBot|HTTrack|HubSpot Crawler|ICC-Crawler|Imperva|IonCrawl|KauaiBot|Kinza|LieBaoFast|Linespider|Linguee|LinkChecker|LinkedInBot|LinuxGetUrl|LMY47V|MacOutlook|Magus Bot|Mail.RU_Bot|MauiBot|Mb2345Browser|MegaIndex|Microsoft Office|Microsoft Outlook|Microsoft Word|MicroMessenger|mindbreeze-crawler|mirrorweb.com|MJ12bot|monitoring-plugins|Monsidobot|MQQBrowser|msnbot|MSOffice|MTRobot|nagios-plugins|nettle|Neevabot|newspaper|Nuclei|OnCrawl|Orbbot|PageFreezer|panscient.com|PetalBot|Pingdom.com|Pinterestbot|PiplBot|python-requests|Qwantify|Re-re Studio|Riddler|rogerbot|RustBot|Scrapy|Screaming Frog|Search365bot|SearchBlox|SearchmetricsBot|searchunify|Seekport|SemanticScholarBot|SemrushBot|SEOkicks|seoscanners|serpstatbot|SessionCam|SeznamBot|Site24x7|siteimprove|Siteimprove|SiteSucker|SkypeRoom|Sogou web spider|special_archiver|SpiderLing|StatusCake|Synack|Turnitin|trendictionbot|trendkite-akashic-crawler|UCBrowser|Uptime|UptimeRobot|UT-Dorkbot|weborama-fetcher|WhiteHat Security|Wget|www.loc.gov|Vagabondo|VelenPublicWebCrawler|Yeti|Veracode Security Scan|YandexBot|YandexImages|YisouSpider|Zabbix|ZoominfoBot" [NC]
RewriteRule ^.* - [F,L]Alternatively, you can make these changes to your docroot/robots.txt or web/robots.txt file:
# Do not index nor follow links that have a query string
# (e.g. /search?page=123 or /search?size=small&color=red)
User-agent: *
Disallow: /*?
# If your views or search pages use a module to convert facets/filters
# to clean URLs (e.g. /search/page/123 or /search/size/small)
# you can try disallowing the search page's URL
User-agent: *
Disallow: /search*Using the file_system service to count files
// In the create method get the file_system service.
$form->fileSystem = $container->get('file_system');
// Search filesystem recursively get all .PHP files from Drupal's core folder.
$files_count = count($this->fileSystem->scanDirectory('core', '/.php/'));See this in action in the examples module in CacheExampleForm.php.
Multiple authors on a node
Thanks to Mike Anello of DrupalEasy for this useful solution.
TL;DR Using the Access by Reference module allows you to specify additional authors via several methods. Mike prefers using a a reference field for this purpose. He also wanted the "Additional authors" field to be listed in the "Authoring information" accordion of the standard Drupal node add/edit form. He created a very small custom Drupal module named multiauthor that implements a single Drupal hook:
/**
* Implements hook_form_alter().
*/
function multiauthor_form_alter(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state, string $form_id): void {
if (in_array($form_id, ['node_page_edit_form', 'node_page_form'])) {
$form['field_additional_authors']['#group'] = 'author';
}
}This hook alters the Basic page add and edit forms, setting my custom "Additional author" field (field_additional_authors) to the "author" group in the "Additional authors" accordion. Users added to the Additional authors field get the same read, update, and delete permissions at the owner of the node.
Calculating, displaying and logging elapsed time
To record how long something takes in Drupal, use the Timer utility class. In the example below, this info is also logged to the watchdog log.
In your config or settings.local.php (to temporarily override that value) you can enable or disable the timer with:
$config['tea_teks_srp.testing']['display_elapsed_time'] = TRUE;
$config['tea_teks_srp.testing']['log_elapsed_time'] = TRUE;This example uses a form so this is the constructor:
class SrpVoteOnCitationForm extends FormBase {
protected bool $displayElapsedTime = FALSE;
protected bool $logElapsedTime = FALSE;
public function __construct(VotingProcessorInterface $votingProcessor) {
$this->displayElapsedTime = \Drupal::config('tea_teks_srp.testing')->get('display_elapsed_time');
$this->displayElapsedTime = \Drupal::config('tea_teks_srp.testing')->get('log_elapsed_time');
}In submitForm() we start the timer, do some work and then stop the timer and report the result like this:
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$user_id = \Drupal::currentUser()->id();
Timer::start('vote:voter_id:' . $user_id);
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();
if ($this->displayElapsedTime) {
$msg = 'Voter: ' . number_format($user_id). ' Citation: ' . number_format($citation_nid) .' Vote: ' . strtolower($voting_action) . ' Url:' . $current_path ;
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage($msg);
}
if ($this->logElapsedTime) {
\Drupal::logger('tea_teks_srp')->info($msg);
}
// do the work...
$end_time_in_ms = Timer::read($timer_name);
Timer::stop($timer_name);
$end_time = number_format($end_time_in_ms / 1000, 4);
$msg = ' Vote: ' . strtolower($voting_action) .' took ' . $end_time . 's' . ' Voter: ' . number_format($user_id) . ' Citation: ' . number_format($citation_nid);
if ($this->displayElapsedTime) {
// Display elapsed time message.
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage($msg);
}
if ($this->logElapsedTime) {
// Log the elapsed time message to watchdog.
\Drupal::logger('tea_teks_srp')->info($msg);
}
// ...Populate a select list with the options from a list field
When you need to build a form with a drop-down (select) list of the options, you can call this function to build the select options that are defined in a list (text) field. You just pass the entity type e.g. node, the bundle or content type e.g. article, and the machine name of the field. You get back a nice array for use in the select list.
Example of list (text) field:
public static function getSelectOptions(string $entity_type, string $bundle, string $field_name): array {
$options_array = [];
$definitions = \Drupal::service('entity_field.manager')->getFieldDefinitions($entity_type, $bundle);
if (isset($definitions[$field_name])) {
$options_array = $definitions[$field_name]->getSetting('allowed_values');
}
return $options_array;
}Then in our form we pass those parameters to get the $audience_select_options:
$audience_select_options = RetrievePublisherData::getSelectOptions('node', 'teks_pub_citation', 'field_tks_audience');Then use the options to populate the form element $form['audience'] like this:
$form['audience'] = [
'#type' => 'select',
'#title' => t('Audience'),
'#empty_value' => '',
'#empty_option' => '- Select the Audience -',
'#required' => TRUE,
'#options' => $audience_select_options,
];Get the human readable value from a list field
When you need to get the human readable value from a list (text) field you can use this code:
call this function to build the select options that are defined in a list (text) field. You just pass the entity type e.g. node, the bundle or content type e.g. article, and the machine name of the field. You get back a nice array for use in the select list.
Example of list (text) field:

This seems to be the simplest version:
public static function getListFieldHumanReadableValue(EntityInterface $entity, string $field_name, string $list_item_value): string {
$allowed_values = $entity->$field_name->getSetting('allowed_values');
$human_readable_value = $allowed_values[$list_item_value];
return $human_readable_value;
}which is called like this:
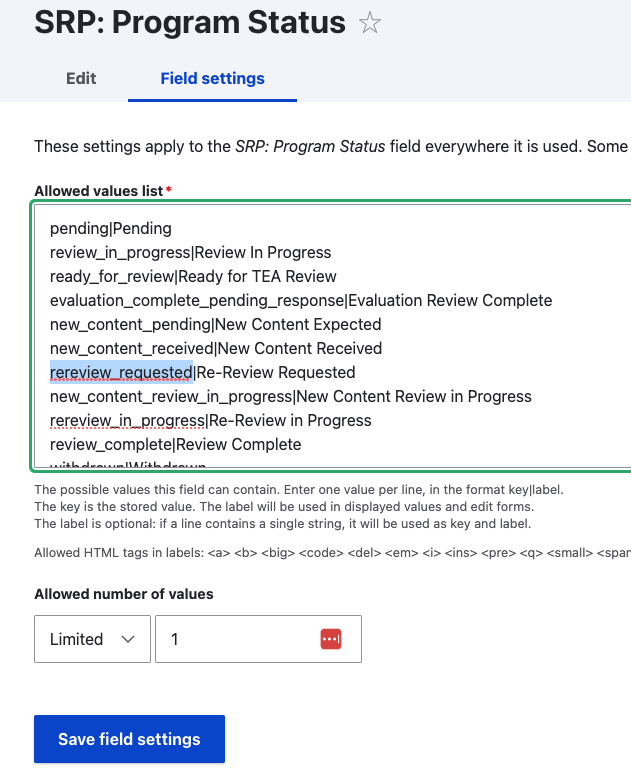
$human_readable_value = VotingUtility::getListFieldHumanReadableValue($program_node, 'field_srp_program_status', 'rereview_requested');$allowed values show up in an indexed array like this:

Some other variations are:
public static function getListFieldHumanReadableValue(EntityInterface $entity, string $field_name, string
// Option 1.
$field = $entity->$field_name;
$human_readable_value = $field->getFieldDefinition()
->getFieldStorageDefinition()
->getOptionsProvider('value', $field->getEntity())->getPossibleOptions()[$list_item_value];
return $human_readable_value;
// Option 2.
// E.g. 'node.article.field_foo'.
$field_string = "node.teks_pub_program.$field_name";
$field_storage_definition = FieldConfig::load($field_string)->getFieldStorageDefinition();
$allowed_values = $field_storage_definition->getSettings()['allowed_values'];
$human_readable_value = $allowed_values[$list_item_value];
return $human_readable_value;
// Option 3.
// E.g. 'node.article.field_foo'.
$field_string = "node.teks_pub_program.$field_name";
$allowed_values = FieldConfig::load($field_string)->getFieldStorageDefinition()->getSettings()['allowed_values'];
$human_readable_value = $allowed_values[$list_item_value];
//$x = $entity->get($field_name)->view()[0]['#markup'];
return $human_readable_value;
}System.schema (module is missing from your site)
When running drush updb, if the system reports:
[notice] Module rules has an entry in the system.schema key/value storage, but is missing from your site. <a href="https://www.drupal.org/node/3137656">More information about this error</a>.
[notice] Module typed_data has an entry in the system.schema key/value storage, but is not installed. <a href="https://www.drupal.org/node/3137656">More information about this error</a>.From https://www.drupal.org/node/3137656
In the database, there is a table called key_value with a field called collection that contains the value system.schema for some rows. The field name has the names of modules.
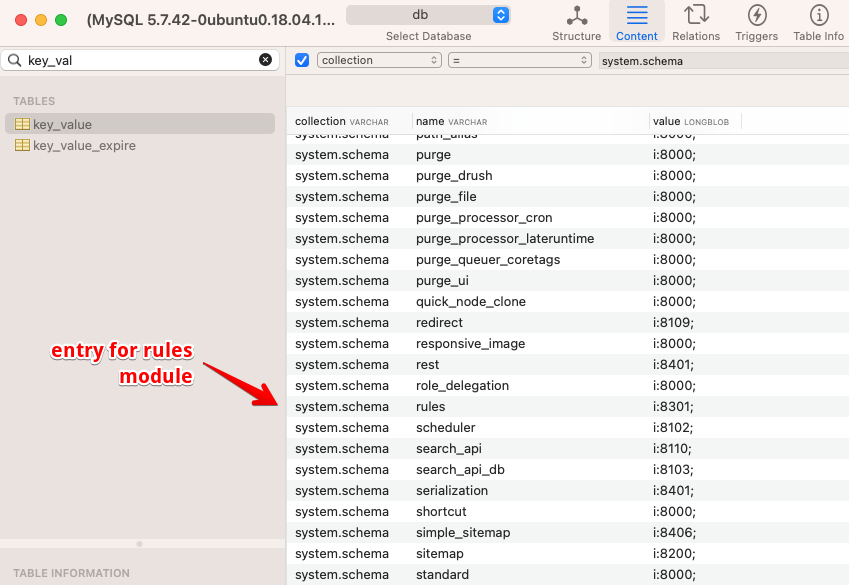
To repair these sorts of errors, you must remove the orphaned entries from the system.schema key/value storage system. There is no UI for doing this. You can use drush to invoke a system service to manipulate the system.schema data in the key_value table. For example, to clean up these two errors:
Module my_already_removed_module has a schema in the key_value store, but is missing from your site.
Module update_test_0 has a schema in the key_value store, but is not installed.You would need to run the following commands:
drush php-eval "\Drupal::keyValue('system.schema')->delete('my_already_removed_module');"
drush php-eval "\Drupal::keyValue('system.schema')->delete('update_test_0');"This can be done using a hook_update_n in your .module file like this:
/**
* Remove the rules and typed_data key/value entries from the system.schema.
*/
function tea_teks_update_8001() {
\Drupal::keyValue('system.schema')->delete('rules');
\Drupal::keyValue('system.schema')->delete('typed_data');
}Alternatively, adding the missing modules with composer install, enabling them and deploying everything to production. Then disabling them properly, deploying that to production, then removing the modules with composer remove and deploying may also work. Of course, this method is a lot more work.
Enable verbose display of warning and error messages
In settings.php, settings.local.php or settings.ddev.php make sure there is the following:
// Enable verbose logging for errors.
// https://www.drupal.org/forum/support/post-installation/2018-07-18/enable-drupal-8-backend-errorlogdebugging-mode
$config['system.logging']['error_level'] = 'verbose';Also see Enable verbose error logging for better backtracing and debugging - April 2023
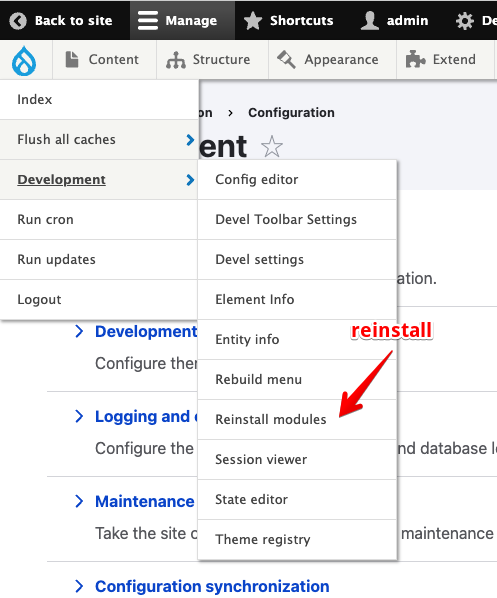
Reinstall modules
During module development or upgrades, it can be really useful to quickly uninstall and reinstall modules. Luckily the devel module provides an easy way. Either navigate to /devel/reinstall or use the Druplicon menu option and select development and then click on reinstall modules You will need the admin toolbar module with it's admin toolbar extra tools submodule enabled.
View a node in JSON format
With the JSON:API and Serialization core modules enabled, simply navigate to any node and add ?_format=api_json to the end of the URL. E.g. https://d9book2.ddev.site/node/25?_format=api_json
Drupal bootstrap process
The Drupal bootstrap process is a series of steps that Drupal goes through on every page request to initialize the necessary resources and environment. Here are the steps:
- Loading the autoloader: The first step in the bootstrap process is to load the Composer-generated
autoloader. This allows Drupal to use any classes defined in the codebase without explicitly requiring the files they're defined in. - Reading settings: Drupal reads the
settings.phpfile which has configuration settings for the site, such as database connection information and various other settings. - Initializing the service container: Drupal initializes the service container which is responsible for managing Drupal services. The service definitions are stored in various
.services.ymlfiles throughout the codebase. Drupal's service container is built on top of the Symfony service container. Documentation on the structure of this file, special characters, optional dependencies, etc. can all be found in the Symfony service container documentation. - Handling the request: Drupal creates a Request object from the global PHP variables and passes it to the
HttpKernelto handle. TheHttpKernelis responsible for handling the request and returning aResponse. - Routing: The
HttpKerneluses the Router service to match the request to a route. A route is a path that is defined for Drupal to return some sort of content on. The route defines a controller that should be used to generate the content for the page. - Controller execution: A method in the controller is then executed. This method generates the content for the page. It can return a render array (which Drupal will turn into HTML), a Response object, or some other type of content that Drupal knows how to handle.
- Rendering: If the controller returns a render array, Drupal will then render it into HTML. This involves calling various hooks and alter functions to allow modules to modify the content.
- Returning the response: Finally, the
HttpKernelreturns a Response object, which is then sent to the client.
Troubleshoot memory problems
In some cases, where there are lots of Node::load() or Node::loadMultiple() calls, you may run into out of memory errors. If increasing the memory limit in php.ini (e.g. memory_limit = 1024M) doesn't resolve this, you might try flushing the entity memory cache with:
\Drupal::service('entity.memory_cache')->deleteAll();There is also a Memory limit Policy module that is worth checking out to override the default memory_limit for specific paths, roles etc.
You can use the memory_get_usage() function to see how much memory is being used. You can also use the memory_get_peak_usage() function to see the maximum amount of memory used during the script's execution.
$mgu1 = round(memory_get_usage() / 1024 / 1024, 2) . ' MB';
$mgu2 = round(memory_get_usage(TRUE) / 1024 / 1024, 2) . ' MB';
$mgpu1 = round(memory_get_peak_usage() / 1024 / 1024, 2) . ' MB';
$mgpu2 = round(memory_get_peak_usage(TRUE) / 1024 / 1024, 2) . ' MB';
\Drupal::logger('tea_teks_srp')->info('Memory usage: ' . $mgu1 . ' ' . $mgu2 . ' Peak: ' . $mgpu1 . ' ' . $mgpu2);Down the rabbit hole:
- Changing PHP memory limits - May 2022
- memory_get_usage()
- memory_get_peak_usage()
- EntityMemoryCache
- gc_collect_cycles - Forces collection of any existing garbage cycles
- Collecting Cycles - reference counting memory mechanisms
